The Apennine chamois (Rupicapra pyrenaica ornata) is an endemic subspecies of the central Apennines, considered one of the rarest and most threatened chamois populations in Europe. After suffering a drastic decline in the 20th century, conservation efforts have enabled a partial recovery of the population, but the reduced numbers and geographic isolation continue to pose a threat to its long-term survival. This project aims to: Analyze the genetic diversity and population structure of the Apennine chamois using the quaddRAD method. Compare the genome
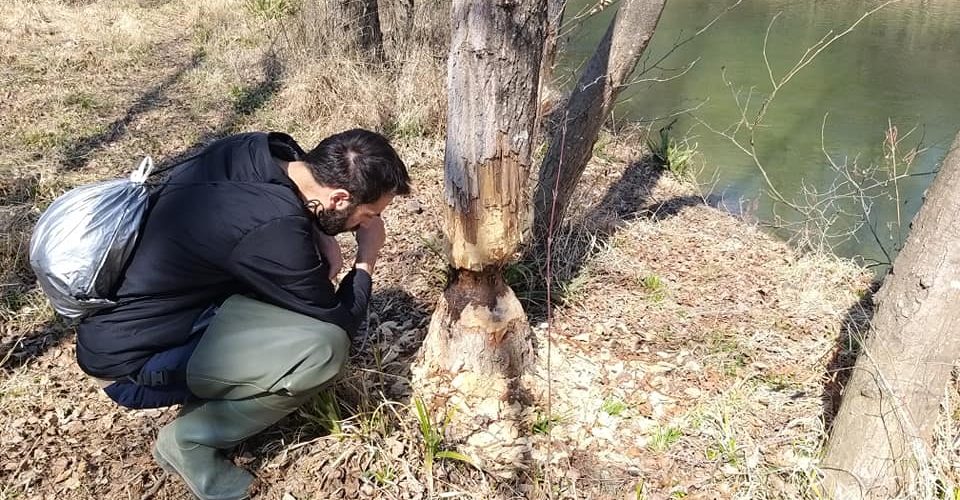
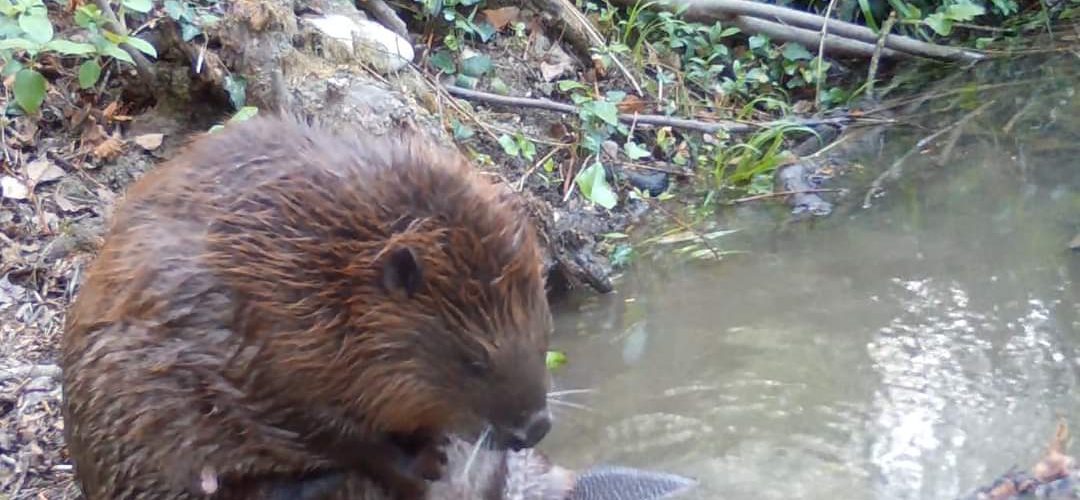
The project “The Beaver’s Legacy” explores the role of the Eurasian beaver (Castor fibre) in biodiversity conservation and ecosystem management in two distinct ecological and social contexts. In Italy, the recent reappearance of the beaver has shown significant benefits for biodiversity, with a positive impact on flora, fauna and water quality, but has also raised questions about the long-term management of the species. In Slovakia, where the beaver has been present for decades, the project addresses the challenges of high
MICROorganism-PLANT Interactions in the Forefield of Glaciers: a Hotspot for Studying the Impact of Climate Change in ALPine Habitats (MICROPLANTALP) During the 21st century, Alpine areas have been experiencing warming at a rate higher than the global average, putting their sensitive ecosystems at risk. Climate change alters the balance between carbon assimilation, storage, and release, potentially leading to significant CO2 emissions. In recent decades, experimental ecology has shifted from observational studies to manipulation experiments, using methods such as soil monolith transplantations
DivAirCity – The power of diversity and social inclusion as a mean for reducing air pollution and achieving green urban nexus in climate neutral cities DivAirCity seeks to redefine urban development by leveraging human diversity as a resource to shape innovative urban services and models for culturally-driven, green cities. The project focuses on the Urban nexus that combines people, places, peace, economic growth, climate robustness and its impact on Air quality and decarbonization. DivAirCity, through citizen science and creativity will co-design
The project aims to select olive cultivars adapted to water-scarce conditions and to develop innovative management strategies based on the use of biostimulants to mitigate the negative effects of climate change. Dendrochronological and dendroisotopic analyses will provide insights into the ecophysiological responses of cultivars to interannual climate variations and the relationships between water use efficiency and plant growth. The results will help identify the most effective combinations of cultivars and biostimulants to enhance olive tree resilience to climate change, contributing to a
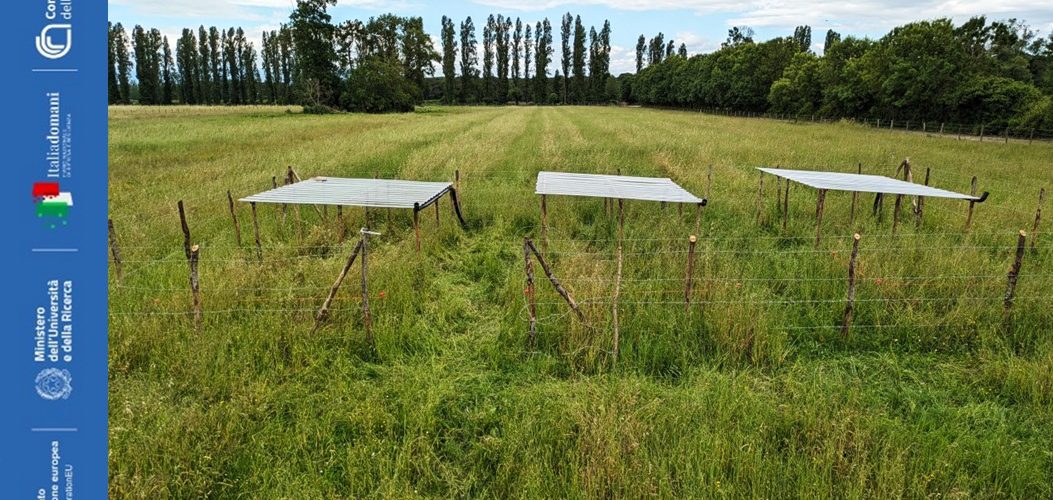
Impact of land use change on climate resilience of semi-natural grasslands (CAROLINA) Loss of grasslands is indicated as one of the primary causes of terrestrial biodiversity impoverishment in the Mediterranean Basin. In Italy this process is realized through the abandonment of traditional agro-pastoral activities with consequent drastic decline of semi-natural grasslands. The success of agro-pastoral impact on the grasslands’ biodiversity and functioning is linked to the tight relationship between the presence of grazing animals, soil edaphic conditions, light availability
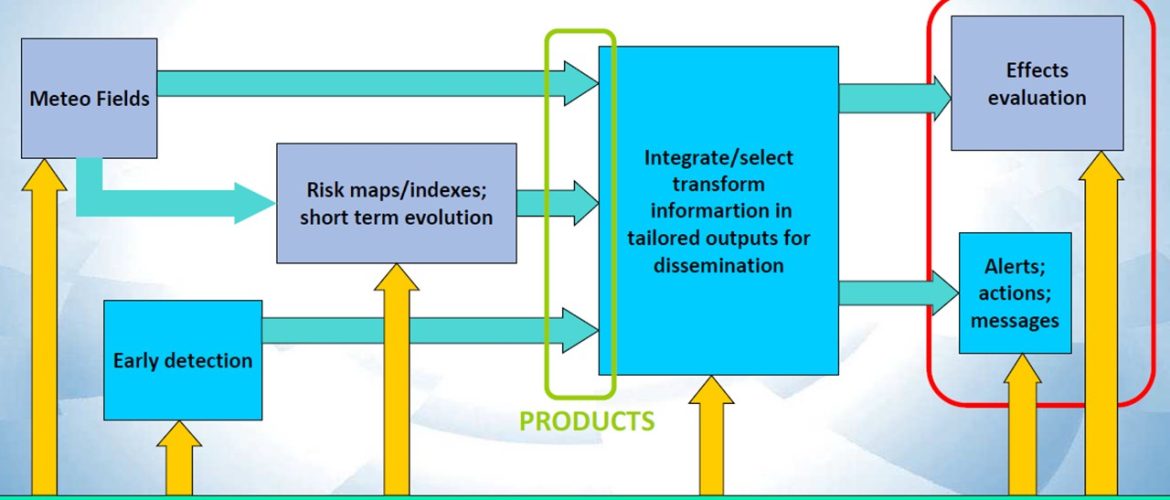
H2020 Arctic Passion: Pan-Arctic Observing System of Systems. Pilot Service: Integrated Fire Risk management (INFRA) Wildfires in the Arctic are primarily ignited by lightning strikes and traditionally left to burn unless they threaten infrastructure or human settlements. However, with the rapid impacts of climate change and the increasing development of Arctic and sub-Arctic regions, this approach is no longer viable. The pilot service focuses on developing an innovative wildfire management service designed to address this growing challenge through three main products: Risk mapping
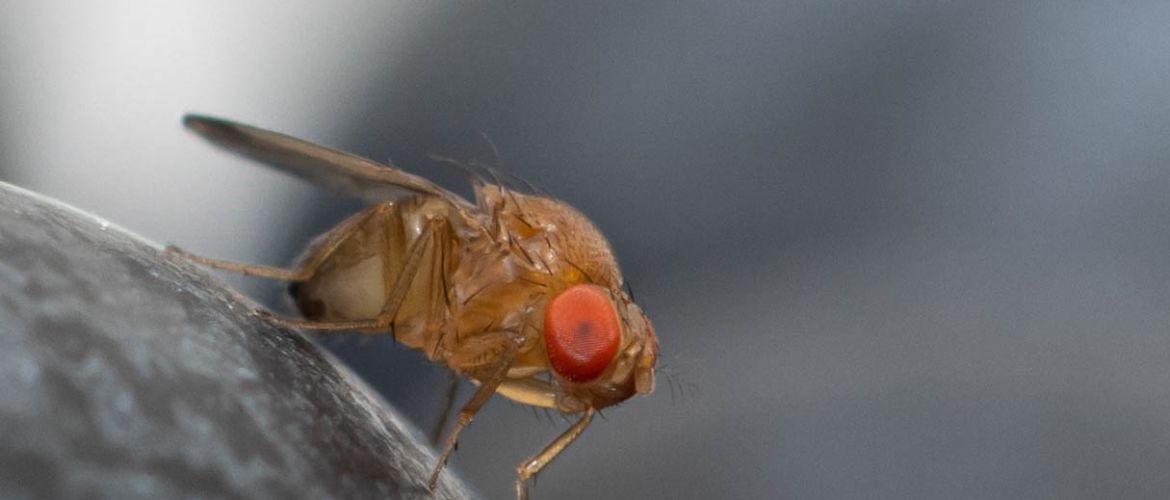
Biological invasions represent one of the greatest threats to global biodiversity today, with negative impacts on human health and the economy of our country. The USEIt project – Using Operational Synergies for the Study and Integrated Management of Invasive Alien Species in ITaly – addresses this issue by initiating a shared process between different marine and terrestrial institutes of the National Research Council (CNR) that aims to improve Italian research on invasive species and transform these environmental challenges into opportunities
The project aims to assess habitat compatibility for the Eurasian beaver (Castor fiber) in Poland and Tuscany by integrating GIS analysis and multi-criteria decision-making approaches (MCDA). As a key ecosystem species, the Eurasian beaver is known for its role in creating wetlands that enhance biodiversity and improve water quality. However, the increasing human impact on riparian areas raises issues of conservation and management. Through the integration of Polish colleagues’ expertise in GIS applications and Italian experience on beaver ecology, the