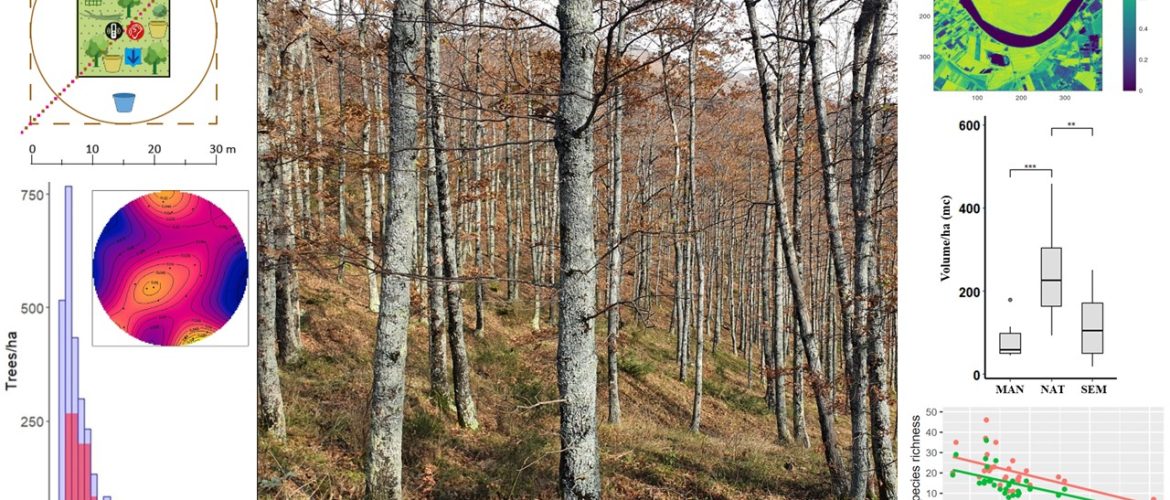
The loss of biodiversity in forest ecosystems is a pivotal issue within the framework of ecosystem adaptation to global changes. The causes are to be found from land-use changes and alterations in biogeochemical balances to biological invasions and extreme climatic events. Unsustainable forest management also leads to excessive simplification of structure and composition. The project aims to investigate the relationship between forest structure and functionality through multi-spatial and multi-temporal analysis and to link it with multi-taxonomic biodiversity (with a particular focus
DIVAS – Developing of Innovative Methods to Assess Tree Vitality After a Wildfire Through Analyses of Cambium Sugars Metabolism The DIVAS project arose from the need to rapidly define the physiological state of plants
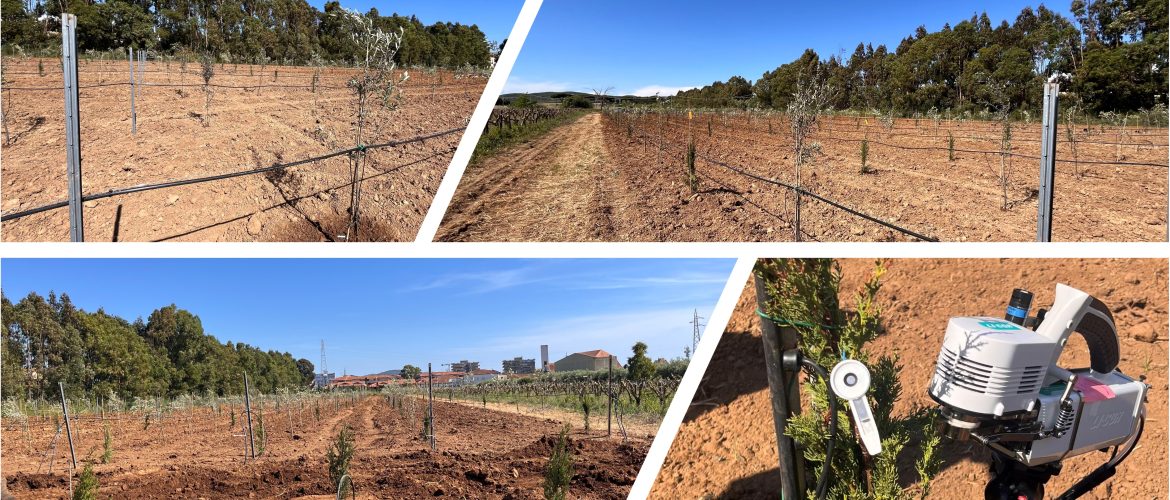
INNO4CFIS – Nature-Based Business Model and Emerging Innovations to enhance Carbon Farming Initiatives (CFIs) while preserving Biodiversity, Water Security and Soil Health The project has two main objectives: 1) to promote reforestation practices (agroforestry) to increase CO2 storage, making more efficient and sustainable use of desalinated water, dryland and soil restoration and promotion of biodiversity, 2) finance highly innovative technologies promoted by small/medium-sized enterprises located in EU countries, in the framework of carbon credit trading. In order to achieve the set objectives, a
TROZGRODIV3 – Tropospheric ozone effects on forest growth and diversity The project continues the activities of previous bilateral projects (TROZGRODIV1&2 ), focusing on the effects of ozone (O₃) on forest growth and diversity. The project aims to refine and optimise the monitoring networks in Italy and Romania to assess the stomatal uptake of O₃ and the occurrence of visible damage, ensuring compliance with the European directives on emissions. It is proposed to evaluate the effectiveness of TreeTalker devices in measuring canopy-level
The 4ClimAir project – Monitoring Italian Forest Vulnerability to Climate Change and Air Pollution of Ozone – aims to analyse and understand in depth the impacts of tropospheric ozone (O₃) and drought on the CO₂ absorption capacity of our forests, the true pillars of Italy’s natural capital, by combining field monitoring and model simulation for a set of forest sites in an innovative way. O₃ is an important greenhouse gas and a fearsome phytotoxic air pollutant for European forests,
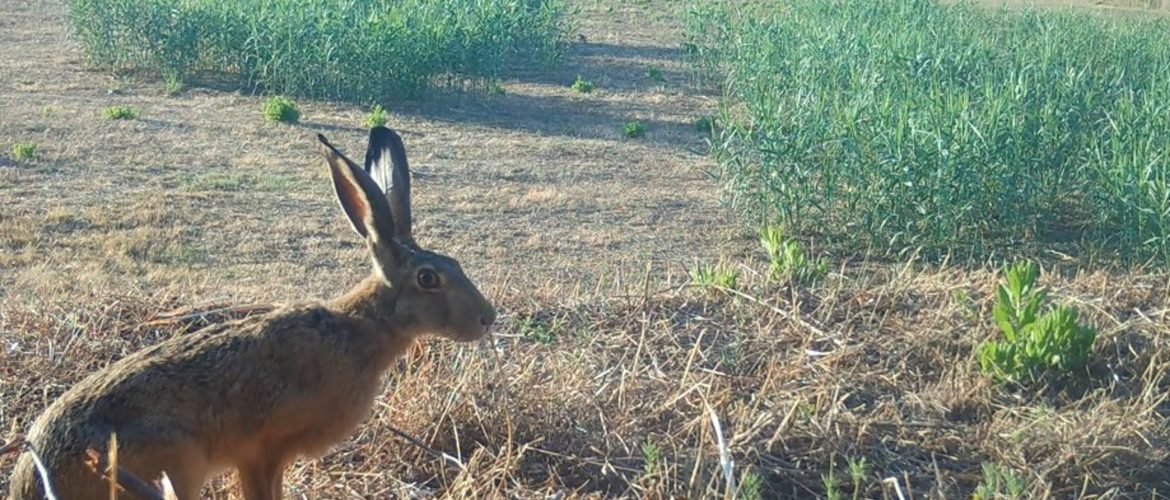
The research project, in the frame of PNRR – NBFC Spoke 5 (Activity 5.2 e 5.4), aims to investigate adaptations, behaviour and interactions between wild mammals in urban and peri-urban contexts, with a focus on small mammals, bats and other species of conservation interest. The initiative combines photo-trapping techniques and the use of hair-tubes to acquire data on the species present, analysing how fragmentation and increasing urbanisation affect biodiversity and animal behaviour.
The LIBRA project – Light Based Multisensing Device for Screening of Pathogens and Nutrients in Bioreactors – introduces an intelligent multi-sensor system for automated on-line screening of cell cultivation processes in bioreactors. The LIBRA detection technology lies in the use of real-time sensors integrated on photonic chips. A new procedure of integrating the photonic platforms together with disposable microfluidic modules and bio-functioning units will result in a modular system with interchangeable components that enable the screening of nutrients and pathogens in
The vertical dimension of conservation: A cost-effective plan to incorporate subterranean ecosystems in post-2020 biodiversity and climate change agenda) – Biodiversa+ Subterranean systems host an extraordinary biodiversity of specialised and endemic organisms, representing a unique portion of global taxonomic, phylogenetic and functional diversity. Moreover, they provide crucial ecosystem services, such as the supply of drinking
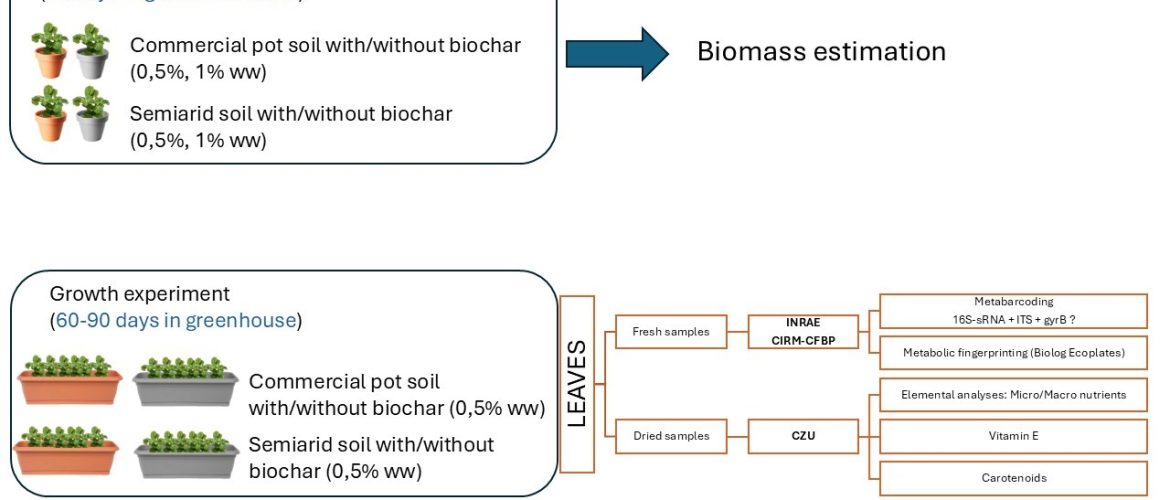
The transnational access project LEMIBIO – Integrating plant quality analysis with LEaf MIcrobiota composition and functional diversity in Chinese cabbage plants grown on BIOchar amended soils – was approved and founded in the frame of the Horizon AgroServ project. Biochar is a high carbon residue produced by the pyrolysis of organic matter. Its potential to improve crop yields and soil properties and functions (e.g. improve soil fertility, soil stability, water retention, carbon sequestration and crop production) has been extensively studied over
The LUCE project – Lighting up the Understudied but Charismatic fireflies of Europe – focuses on the study of fireflies, a charismatic but little-studied species, with a special focus on the hotspot area of the Italian peninsula. In Italy, there are about 20 species of fireflies, which are briefly described. Many of them are endemic and confirmation of their specific status through molecular techniques is crucial for conservation. Indeed, the primary objective is to improve access to taxonomic knowledge through