Traceability of chestnut cultivars using KASP technology for genetic fingerprinting The KasTrack project builds upon the results of the Castarray project (CUP: B21C18000220007), which was carried out by three of the current ten partners (CREA, CNR, and an agricultural company). Castarray focused on developing an economically sustainable method for the
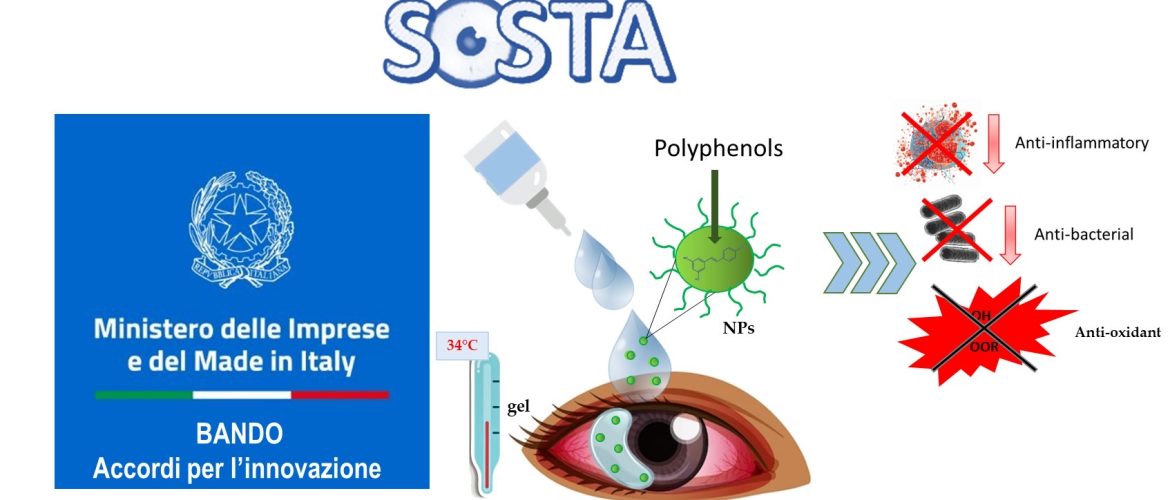
Dry Eye Syndrome (DES) is a multifactorial disease that is growing in incidence, especially in industrialized countries. It manifests as inflammation and damage to the ocular surface caused by a loss of tear film homeostasis. Common symptoms include burning, sandy feeling, photophobia, difficulty opening the eyelids, and, in severe cases, pain and blurred vision. The main causes are decreased tear production or increased evaporation, which leads to an increase in tear film osmolarity and a decrease in calyciform cell
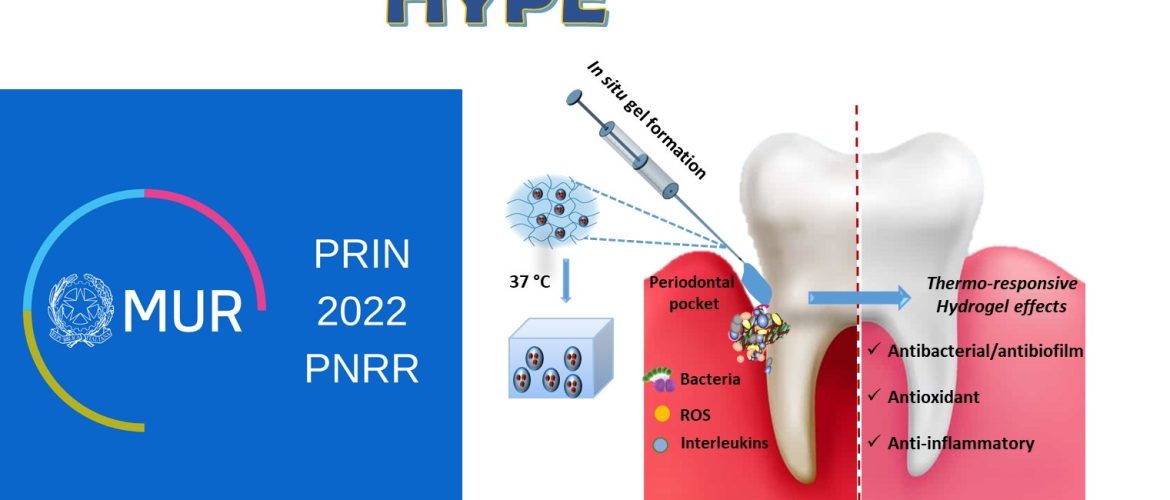
Periodontal disease (PD) is a chronic inflammatory disease of multifactorial etiology, associated with oral dysbiosis (caused by pathogenic bacteria), and characterized by the progressive destruction of the tooth’s supporting apparatus (bone and gums). The incidence of PD in the adult population exceeds 65%, denoting an important public health problem. To date, scaling and root planing (SRP) represents the treatment of choice associated with systemic or localized administration of antimicrobial agents. The use of local antibiotics for long periods may contribute to
The Naples IRET Unit is involved in Spoke 9 – “New Technologies and Methodologies for Traceability, Quality, Safety, Measurements and Certifications to enhance the Value and Protect the typical traits in Agri-food chains” and more specifically in WP1 – Task 1: ‘Chemical, physical, biological and genetic methods and protocols for the quality and traceability of food products’. The research team studies the development of new methodologies and protocols for the evaluation of the quality and application potential of high added-value molecules
The project titled “Lucani tra Ambiente e Salute” – Linea di Intervento 6 – Biosistemi: Ponte tra Ambiente e Salute aims to carry out a multidisciplinary study focused on the characterization of environmental matrices. The findings will assess the degree of anthropogenic pollution capable of inducing variations in ecosystem services that, in turn, could negatively affect human health. The proposed intervention arises from the need to provide information on natural and anthropogenic pollution sources affecting a specific territory, with the goal
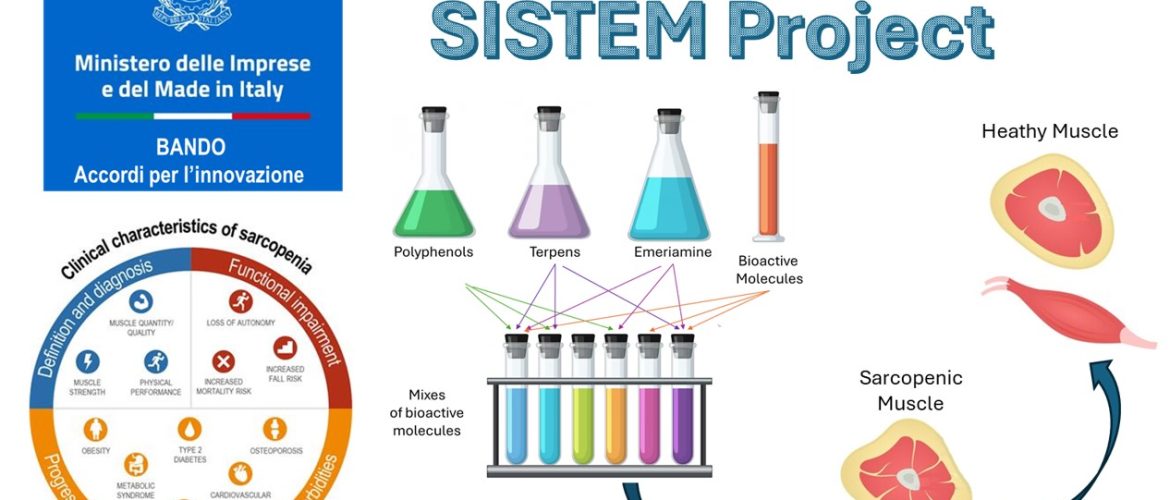
The SISTEM project – Sarcopenic syndrome with multimorbidity: prevention and management of chronic disease with synergistically acting bioactive molecules of natural origin – funded by MiSE, aims to develop a mixture of natural-derived bioactive molecules with synergistic activity in counteracting the effects of sarcopenic muscle decay even in the presence of comorbidities. Sarcopenia is now recognized as a multifactorial disease, linked to the interaction of multiple mechanisms, including muscle pathophysiological changes related to the aging process, lifestyle, exposure to anthropogenic pollutants,
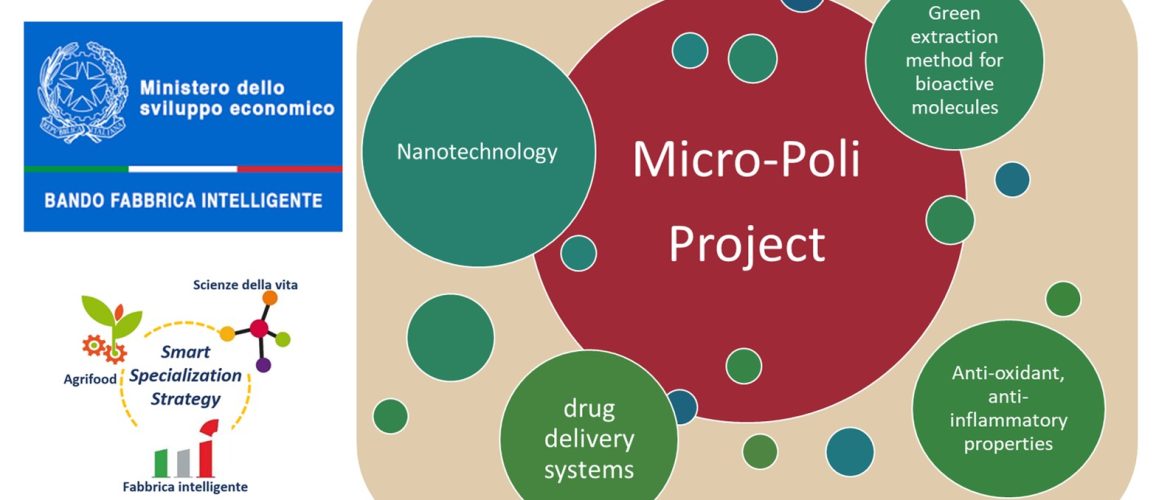
The MICROPOLI project “Micro-nanodispositivi veicolanti polifenoli isolati da scarti della filiera olivicola come nuovi integratori alimentari”, funded by MiSE, by using nanotechnology, aims to develop and industrialize micro-nanostructured systems capable of increasing the bioavailability of bioactive molecules (such as polyphenols) extracted from agro-industrial waste (e.g., waste produced during the final stages of extra virgin olive oil – EVOO – production). In recent years, many efforts have been made, with limited success, to develop formulations containing bioactive molecules characterized by high physical
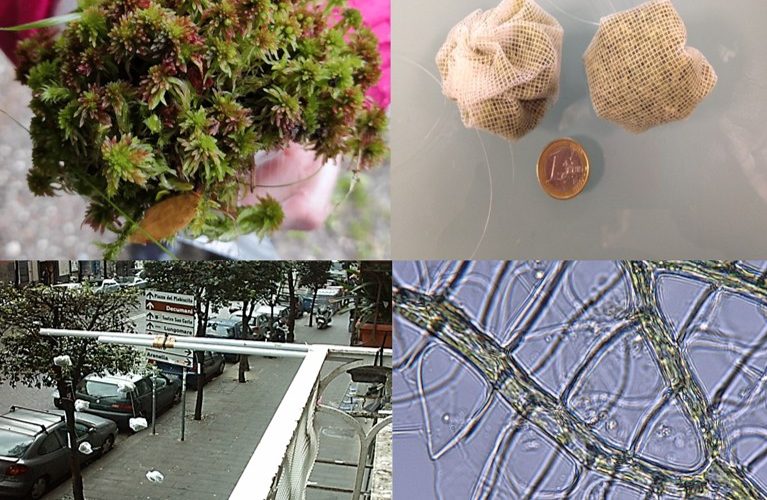
Topic 1 – Biomonitoring: plants, particularly mosses, are considered as bioindicators and bioaccumulators of biological compounds and pollutants, characterized both qualitatively (e.g., electron microscopy) and quantitatively (e.g., mass spectrometry). Among the methods, mosses can be used as transplants in “moss bags” to be exposed at monitoring sites. Topic 2 – Bioadsorption: the chemical-physical properties of moss surfaces are studied through in vitro experiments, analysis of surface functional groups, and chemical-physical determination of the surface area, aiming to study plant-pollutant
Ecosystem functions, services and solutions – PNRR, NBFC, Spoke 4 Task 4.3 – Genetic-molecular and modeling approaches for the development of application tools for the conservation of ecosystems of special value. Subtask 4.3.1 – Genetic-molecular approaches. In accordance with the aims of NBFC we (1) estimate the neutral and adaptive variability of forest tree species in the Mediterranean environment, highlight any critical issues (e.g. fragmentation, erosion of gene pool, inbreeding); (2) provide new tools for the medium and long-term management and conservation of
Sicilian woods, despite representing less than 10% of the regional territory, host one of the richest dendrofloras in Italy and include numerous species of great biogeographical, natural and economic interest. Often the species are at the southern limit of the range, adapted to different climatic conditions, and therefore with a potential importance for reforestation and conservation in an increasingly alarming scenario of global warming. We study the intra- and inter-population diversity of different woody species. We sampled Acer platanoides, very rare in